January 30, 2016
As the need for increased network bandwidth to meet the global IP traffic demand is growing rapidly, there is an urgent need for upgrading to 40G Ethernet links in data centers. And the IEEE 802.3ba committee has already ratified the 40 Gigabit Ethernet standard and along with the general specification, defining a number of fiber optic interfaces. These standard interfaces attempted to satisfy a number of different objectives including support for multi-mode fiber (MMF) and single mode fiber (SMF) compatibility. Therefore, there appears various transceiver solutions for migrating to 40G Ethernet network. Among these solutions, there are three popular ones: 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceiver, 40G SR4 QSFP+ transceiver and 40G QSFP+ BiDi transceiver. This article will give a comprehensive comparison on them.
40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers are hot-swappable Ethernet optical transceivers that support high-speed serial links over single mode optical fiber. With built-in optical multiplexing and de-multiplexing, this kind of transceiver has four channels of 10G multiplexed/de-multiplexed inside the module to transmit and receive an aggregate 40G signal over a single pair (2 strands) of fiber. Used with LC connectors and single mode fiber, 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers’ transmission distance can cover around 10km.
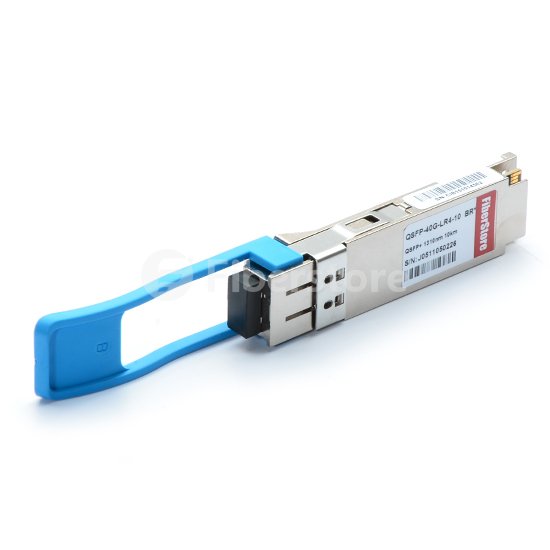
As 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers can be used together with LC connectors, they may use existing duplex fiber infrastructure for 40G migration. That’s to say, 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers can offer a very cost effective connectivity solution and unique value proposition for data centers to migrate from 10G to 40G Ethernet network with minimal disruption with existing fiber optical infrastructure. The main disadvantage of 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers is that the optical link may not be as simple as that of 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers. The following is a picture of FinisarFTL4C1QE1Ccompatible 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver.

40G SR4 QSFP+ transceivers are parallel fiber optical module with four independent optical transmit and receive channels. Each of these channels is capable of a 10G operation for an aggregate data rate of 40G. These transceivers use MTP/MPO connectors and require multi-mode OM3 or OM4 cables. They can support with a link length up to 100 meters on OM3 cable and 150 meters on OM4 cable.
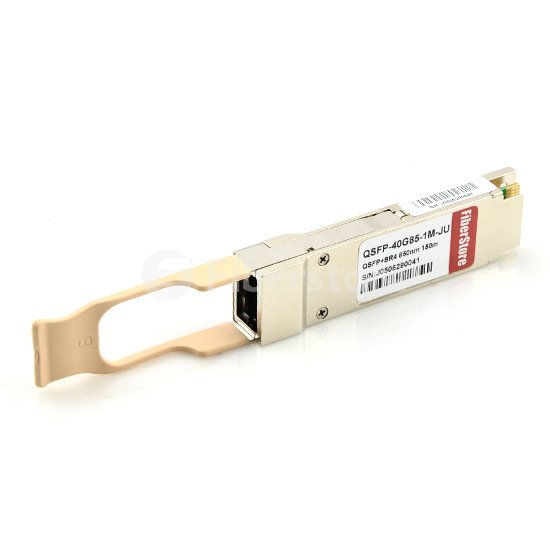
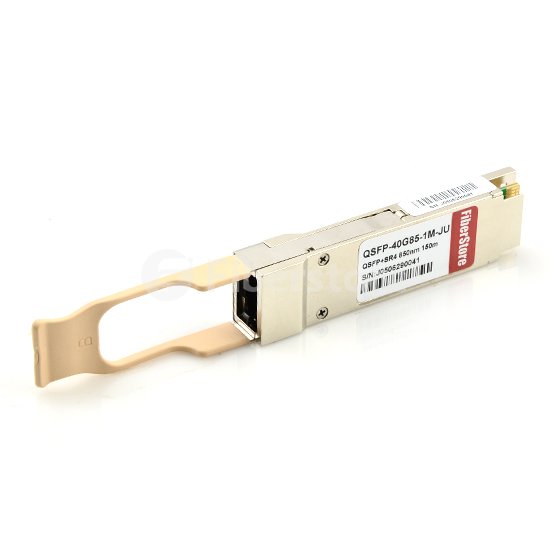
40G SR4 QSFP+ transceivers use fundamentally different connectivity formats, requiring fiber cabling infrastructure to be redesigned and replaced. Thus, they cannot reuse aggregation fiber infrastructure built for 10-Gbps connectivity. The following is a picture of CiscoQSFP-40G-SR4compatible 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver.

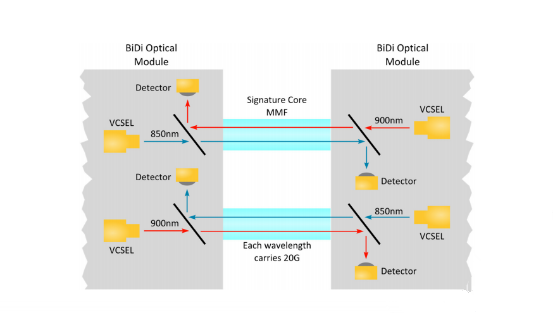
40G QSFP+ BiDi transceivers are the lasted products used in 40G transmission. They are transceivers that transmit full-duplex 40-Gbps traffic over one dual-fiber LC-connector OM3 or OM4 MMF cable. 40G QSFP+ BiDi transceivers have two 20Gbps channels, each transmitted and received simultaneously over two wavelengths on a single MMF strand. The result is an aggregated duplex 40Gbps link over a MMF duplex LC-terminated fiber cable. The connection can reach 100 meters on OM3 MMF or 150 meters on OM4 MMF, which is the same as 40Gbps SR4. The following figure shows the technology concept of the Cisco QSFP BiDi transceiver.
To accommodate an ever increasing spectrum of 40 Gigabit Ethernet applications, Fiberstore offers various 40GBASE QSFP+ transceiver types, suitable for different media and distance reaches. All of our QSFP+ transceivers are tested in-house prior to shipping to ensure that they will arrive in perfect physical and working condition. We offer our customers with high-performance and cost-effective products to fulfill their requirements, contributing this way to the customer's success and satisfaction.
Posted by: jowang at
03:26 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 583 words, total size 6 kb.
As the need for increased network bandwidth to meet the global IP traffic demand is growing rapidly, there is an urgent need for upgrading to 40G Ethernet links in data centers. And the IEEE 802.3ba committee has already ratified the 40 Gigabit Ethernet standard and along with the general specification, defining a number of fiber optic interfaces. These standard interfaces attempted to satisfy a number of different objectives including support for multi-mode fiber (MMF) and single mode fiber (SMF) compatibility. Therefore, there appears various transceiver solutions for migrating to 40G Ethernet network. Among these solutions, there are three popular ones: 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceiver, 40G SR4 QSFP+ transceiver and 40G QSFP+ BiDi transceiver. This article will give a comprehensive comparison on them.
40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers are hot-swappable Ethernet optical transceivers that support high-speed serial links over single mode optical fiber. With built-in optical multiplexing and de-multiplexing, this kind of transceiver has four channels of 10G multiplexed/de-multiplexed inside the module to transmit and receive an aggregate 40G signal over a single pair (2 strands) of fiber. Used with LC connectors and single mode fiber, 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers’ transmission distance can cover around 10km.
As 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers can be used together with LC connectors, they may use existing duplex fiber infrastructure for 40G migration. That’s to say, 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers can offer a very cost effective connectivity solution and unique value proposition for data centers to migrate from 10G to 40G Ethernet network with minimal disruption with existing fiber optical infrastructure. The main disadvantage of 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers is that the optical link may not be as simple as that of 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers. The following is a picture of Finisar FTL4C1QE1C compatible 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver.

40G SR4 QSFP+ transceivers are parallel fiber optical module with four independent optical transmit and receive channels. Each of these channels is capable of a 10G operation for an aggregate data rate of 40G. These transceivers use MTP/MPO connectors and require multi-mode OM3 or OM4 cables. They can support with a link length up to 100 meters on OM3 cable and 150 meters on OM4 cable.
40G SR4 QSFP+ transceivers use fundamentally different connectivity formats, requiring fiber cabling infrastructure to be redesigned and replaced. Thus, they cannot reuse aggregation fiber infrastructure built for 10-Gbps connectivity. The following is a picture of Cisco QSFP-40G-SR4 compatible 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver.

40G QSFP+ BiDi transceivers are the lasted products used in 40G transmission. They are transceivers that transmit full-duplex 40-Gbps traffic over one dual-fiber LC-connector OM3 or OM4 MMF cable. 40G QSFP+ BiDi transceivers have two 20Gbps channels, each transmitted and received simultaneously over two wavelengths on a single MMF strand. The result is an aggregated duplex 40Gbps link over a MMF duplex LC-terminated fiber cable. The connection can reach 100 meters on OM3 MMF or 150 meters on OM4 MMF, which is the same as 40Gbps SR4. The following figure shows the technology concept of the Cisco QSFP BiDi transceiver.

To accommodate an ever increasing spectrum of 40 Gigabit Ethernet applications, Fiberstore offers various 40GBASE QSFP+ transceiver types, suitable for different media and distance reaches. All of our QSFP+ transceivers are tested in-house prior to shipping to ensure that they will arrive in perfect physical and working condition. We offer our customers with high-performance and cost-effective products to fulfill their requirements, contributing this way to the customer's success and satisfaction.
Posted by: jowang at
03:26 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 587 words, total size 6 kb.
January 29, 2016
Written by Scott Bicheno

Industry support of the unique self-interference cancelling technology developed by Kumu Networks increased with a Series C funding round led by leading telecoms players.
Cisco, Verizon Ventures, Deutsche Telekom Strategic Investments, and Swisscom all had a whip-round to raise $25 million and hand it over to Kumu to help it keep up the good work. Kumu’s technology claims to enable full-duplex transmission, allowing full utilization of one frequency for both sending and receiving at the same time – potentially doubling spectral efficiency.
"Kumu Networks’ full-duplex technology is a rare technological breakthrough that offers substantial benefit to a multitude of wireless modalities,†said Rachid El Hattachi, SVP Architecture and Blueprints at DT. "Full-duplex offers significant advantages and removes roadblocks from wireless endeavours as diverse as LTE Advanced, general Radio Frequency planning and future standards and protocols. We jumped at a chance to invest in and help foster this important new technology.â€
"Full-duplex technology can simplify difficult network expansion tasks and increase spectral efficiency,†said Vijay Doradla, director at Verizon Ventures. "We look forward to Kumu Networks’ continued growth as they seek to commercialize their technology for near-term applications in the wireless ecosystem.â€
"We are honoured to have such a broad coalition of investors participating in our Series C funding,†said Kumu Networks CEO David Cutrer. "The diverse group of investors highlights the broad reach and economic potential of our solution and its massive impact on multiple arenas within the wireless industry.â€
In addition TIM (Telecom Italia) has just carried out what it claims is the world’s first test of ‘full-duplex relay’ technology in Turin, in partnership with Kumu. "We are very happy to announce this first ‘live’ test,†said Gabriela Styf Sjoman, Head of TIM’s Engineering & TILAB. "5G is a key network evolution towards more advanced digital services and we are not only committed to defining the standards, but also to contributing to key research and development initiatives that will be fundamental for a healthy ecosystem in digital services, including the network, open platforms and services.â€
Incidentally Verizon has also chosen to join the ONOS project, which has the stated aim of keeping SDN development open. "Verizon recognizes the potential of ONOS as an open source SDN platform and the service provider solutions it enables, as well as the promise it holds to transform the networking industry,†said Brian Higgins, VP of Network Planning at Verizon. "By joining the partnership, we hope to advance open source SDN and NFV solutions based on ONOS and to help shape the future of this ecosystem.â€
Cisco, meanwhile, has also chosen to invest in IoT platform startup Kii, although Cisco insists on calling it IoE (Internet of Everything) instead. "Building compelling mobile and IoE solutions requires a multifaceted effort – and the backend platform is one of the key ingredients,†said Miyuki Suzuki, president of Cisco Systems G.K. "We believe our investment in Kii will help support the development of a platform that offers the ease of use, features and scalability needed to bring IoE solutions to market rapidly.â€
Posted by: jowang at
02:27 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 521 words, total size 5 kb.
January 27, 2016
40 Gigabit Ethernet is now being widely adopted within data centres. The demand for high data rates has come a long way since the ratification of the IEEE standard in 2010 and as this demand has increased so has the requirement for suitable cabling infrastructure. 40GBASE-SR4 laser optimized OM3 or OM4 fibre cable is one cabling option for 40 Gigabit Ethernet. What is 40GBASE-SR4? The following passage mainly talks about things you need to know about 40GBASE-SR4.
40GBase-SR4 is an interface for 40 Gigabit Ethernet. It is a fiber optic interface for multimode fiber of OM classes 3 and 4 with four parallel OM3 or OM4 fibers in both directions. "S" means short, indicating that it is an interface for short distances. The "R" denotes the type of interface with 64B/66B encoding and the numeral 4 indicates that the transmission is carried out over a ribbon fiber with four multimode fibers in every direction. Each lane has a 10 Gbit/s data rate. The distance depends on the OM class of multimode fiber, up to 100m and 150m on OM3 and OM4 fibers respectively.
40GBase-SR4 uses OM3 and OM4 laser-optimized multimode optical fibers for short reach 40 Gigabit Ethernet applications. OM3 and OM4 are laser-optimized 50/125 µm multimode optical fibers. Lasers are used as signal sources for category OM3 and OM4 fibers. These lasers are generally vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs). This type of laser is considerably cheaper than, for example, Fabry-Perot lasers or distributed feedback lasers. Lasers have the advantage of being able to transmit data at higher rates. The 802.3ba standard defines the parallel operation of four OM3/OM4 fibers for 40 GbE in 40GBASE-SR4. Two fibers have to be used per link because this arrangement is full duplex operation, i.e. simultaneous transmission in both directions. Therefore the number of fibers increases to eight for 40GBASE-SR4.
40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ (quad small form factor pluggable) modules usually use a parallel multimode fiber (MMF) link to achieve 40G. It offers 4 independent transmit and receive channels, each capable of 10G operation for an aggregate data rate of 40G over 100 meters of OM3 MMF or 150 meters of OM4 MMF. These transceivers house an MPO (usually an MTP) connector and are connected to other 40G ports or to 10G ports after the 40G signal is split to four channels. MPO/MTP connector provides a smooth transition to higher Ethernet speeds with minimum disruption and without wholesale replacement of existing cabling and connectivity components. An MPO/MTP connector has either 12-fiber or 24-fiber array. For 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver, a MPO connector with 12 fibers is used. 10G is sent along each channel/fiber strand in a send and receive direction and only 8 of the 12 fibers are required. The picture below shows a Juniper QFX-QSFP-40G-SR4 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver.
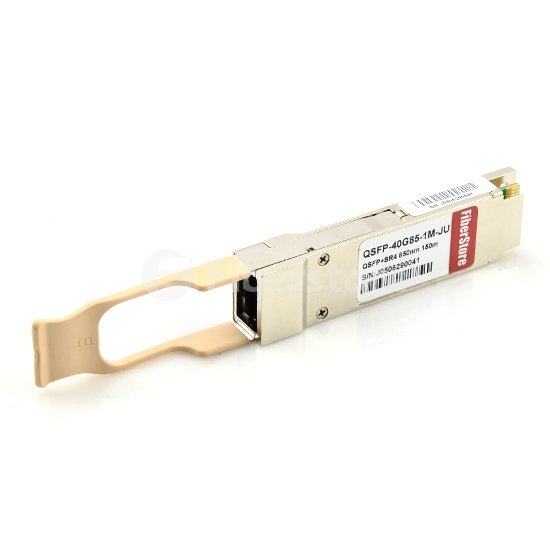

Fiberstore offers 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver for data centers and other high performance networking purposes. Our 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver is available in a wide variety of features to accommodate 40 Gigabit Ethernet datacom and telecom fiber networking applications. Fiberstore 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceivers are customized to function as a cost effective alternative compatible with most major brands, including Cisco, Juniper, Arista, Brocade, HP, Intel, and Extreme. Our hot-pluggable optical transceivers can help you achieve significant savings in operating costs while also maintaining a reliable networking backbone.
Posted by: jowang at
07:24 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 559 words, total size 5 kb.
January 25, 2016
In today's server networks, 10GbE (Gigabit Ethernet) has become commonplace. However, for some workloads, 10GbE might not be enough. As data centers virtualize more of their servers and storage, the need for speedy network connections increases. Believe it or not, the 40GbE (Gigabit Ethernet) era is already upon us. The standard has long been ratified, and products are shipping. However, there has been some debate as to whether IT managers should hold off on deploying the 40GbE technology and bide their time waiting for 100GbE to become commercially available. Why should we choose 40GbE?
40GbE is an Ethernet standard developed by the IEEE 802.3ba Task Force that support sending Ethernet frames at 40 gigabits per second. It also addresses physical layer specifications for communication across backplanes, copper cabling, multi-mode fiber and single-mode fiber. At the heart of the 40GbE network layer is a pair of transceivers connected by a cable, for example OM4 or OM3 fiber cable. The transceivers, in turn, are plugged into either network servers or a variety of components including interface cards and switches. 40GbE is becoming commonly applied to access links to connect servers as Figure 1 indicates.
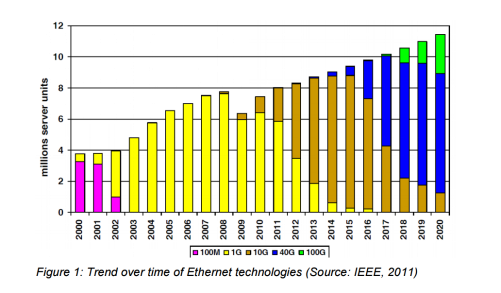
40GbE can be effectively deployed today in aggregation links in data center networks. The standards for 40 GbE have been around as a specification, and a number of routers, switches, and network cards already operate at this speed. Vendors such as Cisco, Dell’s Force10, Mellanox, HP, Extreme Networks, Finisar, and Brocade offer such hardware. And another attractive characteristic of 40GbE is broad applications and design flexibility. Considering the productivity gains and decrease in operating expense (OPEX), migrating to 40GbE will prove very cost-effective for those who do it right.
In migrating to 40GbE, some networks will be able to use their current 10GbE switch chassis and just upgrade their line cards and transceivers. Deploying a QSFP+ form factor transceiver will provide the flexibility to migrate from 10GbE to 40GbE. With regards to cabling, OM3 or OM4 is optimal for the 40GbE or 100GbE data center environment. The major difference is in the maximum span distances. In a 10GbE network, OM3 fiber can span up to 300m while OM4 supports even longer channels. In a 40GbE or 100GbE environment, OM3 can be used up to 100m and OM4 up to 150m according to the IEEE802.3ba standard. For applications approaching 150m, the cable should be terminated with low loss connectors.
It is like building an eight-lane superhighway with dirt off ramps and interchanges. Unless you upgrade everything, it is totally useless. You bump into things like immature network interface card drivers that can hang up your entire system. 40GbE is like a bridge which enbales you to prepare for higher needs. Fiberstore is a professional manufacturer and supplier of a complete range of 40GbE transceiver modules and cables. We provide compatible QSFP+ transceivers as alternatives to those branded by Cisco, HP, Juniper, Brocade, Finisar and so on. For example, Brocade QSFP+ and Finisar QSFP+ offer by us are high-performance and cost-effective products to fulfill your requirements.
Posted by: jowang at
04:13 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 520 words, total size 5 kb.
January 21, 2016
10 Gigabit Ethernet is no longer enough for the increasing need for high speed transmission with applications like Big Data, Cloud and Internet of Things being introduced in a variety of industries. Transmission network migration to 40G has already been the industry consensus. Juniper QSFP+ (quad small form-factor pluggable plus) modules offer you a wide variety of connectivity options for your 40 Gigabit Ethernet applications. This article introduces several kinds of Juniper 40GBASE QSFP+ modules to you.
Juniper is a leading provider of optical and copper network equipment including all kinds of optical transceivers and cables. Juniper QSFP+ is a Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) standard for high speed application, providing four channels of data in one pluggable interface. Each channel is capable of transferring data at 10Gbps and supports a total of 40Gbps. Juniper 40G QSFP+ transceivers are QSFP+ MSA and SFF-8436 compatible and are electrically hot-pluggable, with four independently addressable transmit and receive channels. Juniper QSFP+ transceivers are well tested on Juniper switch to ensure optimal signal integrity and the best end-to-end performance. The following part will introduce three types of Juniper QSFP+ modules.
Juniper JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver supports link lengths of up to 10km over single mode fiber with duplex LC connectors. 40 Gigabit Ethernet signal is carried over four wavelengths. Multiplexing and demultiplexing of the four wavelengths are managed in the device. It is compliant with the QSFP+ MSA and IEEE 802.3ba, and RoHS-6 compliant with built-in DDM interface. Juniper JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 QSFP+ module can also be used in a 4x10G module for interoperability with 10GBASE-LR interfaces. The image below shows a Juniper JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 compatible 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver.

Juniper JNP-QSFP-40G-LX4 40GBASE-LX4 QSFP+ transceiver supports link lengths of up to 300m on OM3 multi-mode fiber (MMF). It is compliant with QSFP+ MSA, RoHS, and QDR/DDR Infiniband data rates. It is designed with form factor, optical/electrical connection and digital diagnostic interface according to the QSFP+ MSA. It has been designed to meet the harshest external operating conditions including temperature, humidity and EMI interference. The image below shows a Juniper JNP-QSFP-40G-LX4 40GBASE-LX4 QSFP+ transceiver.

Juniper QFX-QSFP-40G-SR4 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver supports link lengths of 100m on OM3 multimode fibers and 150m and OM4 multimode fibers, operating at a wavelength of 850nm. The image below shows a Juniper QFX-QSFP-40G-SR4 compatible 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver. It enables high-bandwidth 40G optical links over fiber terminated with MPO/MTP multifiber connectors and can also be used in a 4x10G module for interoperability with 10GBASE-SR interfaces. It is the standard MSA multi-mode transceiver for 10Gigabit Ethernet and 40Gigabit Ethernet with MPO connector.

Fiberstore is able to provide customized and cost-effective solutions of high quality for all needs and specifications. We offer various kinds of 40GBase QSFP+ transceivers branded by many famous companies. Juniper QSFP+ transceivers provided by Fiberstore are the most cost-effective standards-based QSFP+ modules. They are 100% compatible with major brands and backed by a lifetime warranty.
Posted by: jowang at
03:30 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 493 words, total size 6 kb.
January 18, 2016
With the growing demand for high-performance computing among end users, and increasing need for faster data transfer rates, the business case for 40 Gigabit Ethernet is becoming inescapably compelling. The biggest market for 40G Ethernet (40GbE) is in data center for interconnection links with servers and storage area networks. How to deploy 40G Ethernet? This post gives some basic information about 40G cabling and transceivers.
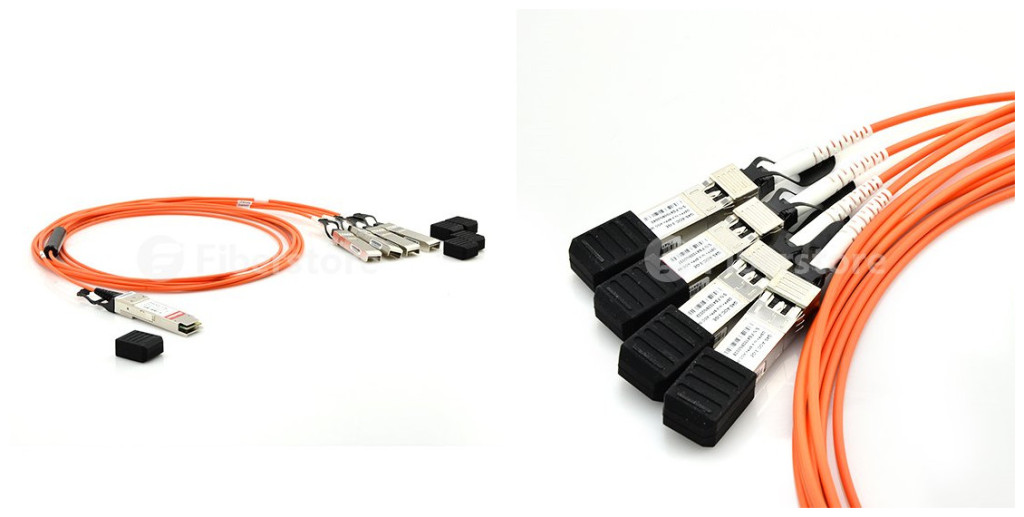
When it comes to cabling choices for 40G applications, fiber optic cable is a good choice in many aspects. OM3 or OM4 is optimal for the 40 Gigabit Ethernet data center environment. In a 40 Gigabit Ethernet environment, OM3 can be used up to 100m and OM4 up to 150m, according to the IEEE802.3ba standard. OM3 and OM4 multimode cabling is generally recommended because its reach supports a wider range of deployment configurations compared to copper solutions, and the cost is lower compared to single-mode solutions. 40G active optical cable for 40GbE applications is terminated with 40GBASE QSFP+ transceiver on one end while on the other end, it can be terminated with QSFP+ connector, SFP+ connector, or LC/SC/FC/ST connector. Active optical cable uses electrical-to-optical conversion on the cable ends to improve speed and distance performance of the cable without sacrificing compatibility with standard electrical interfaces. QSFP+ AOC integrates four data lanes in each direction with 40Gbps aggregate bandwidth. Each lane can operate at 10Gbps with lengths ranging from one to 100m. It is compliant with the QSFP MSA and IEEE P802.3ba. The following picture shows a Cisco QSFP-4X10G-AOC10M compatible QSFP+ to 4SFP+ active optical cable.
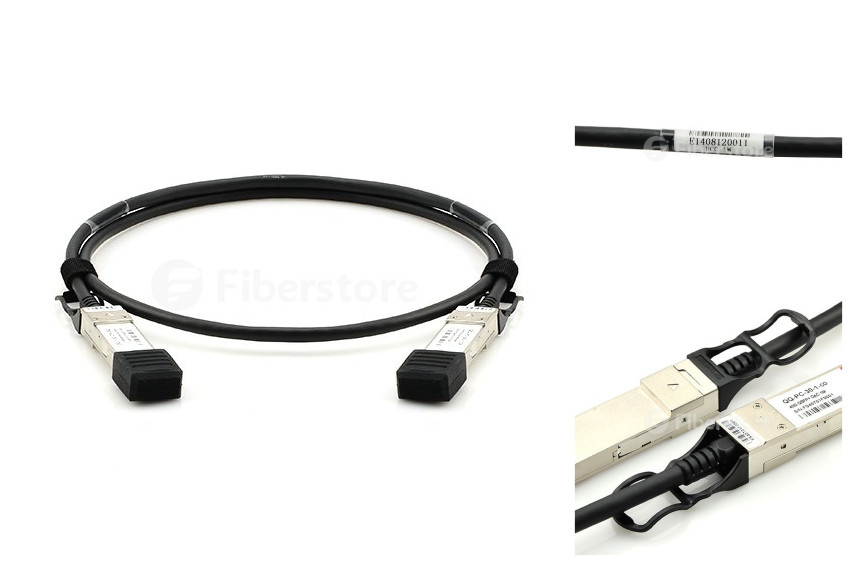
Other than fiber optic cabling, you still have another choice for your 40G applications, which is 40G direct attach copper cable (DAC). There are active DACs and passive DACs. Passive copper cables are preferred alternative for short-reaches in the data center. QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) copper cable assemblies were developed for high-density applications, offering a cost-effective, and low-power option for high speed data center interconnects up to 10 meters. 40GbE passive copper cables provide robust connections for leading edge 40G systems and have extremely low power consumption which improves data center power consumption and thermal efficiency which are ideal for 40G LAN, HPC and SAN applications. QSFP+ to QSFP+ passive copper cable and QSFP+ to 4SFP+ passive breakout copper cable are the two common types of QSFP+ cables. Fiberstore provides QSFP+ to QSFP+ passive copper cables of different lengths branded by many famous companies like Cisco, Juniper, and HP. For example, Cisco QSFP-H40G-CU1M, QSFP-H40G-CU3M, and QSFP-H40G-CU5M compatible QSFP+ to QSFP+ passive copper cables are 1m, 3m and 5m options. The picture below shows a 1m Cisco QSFP-H40G-CU1M passive copper cable.

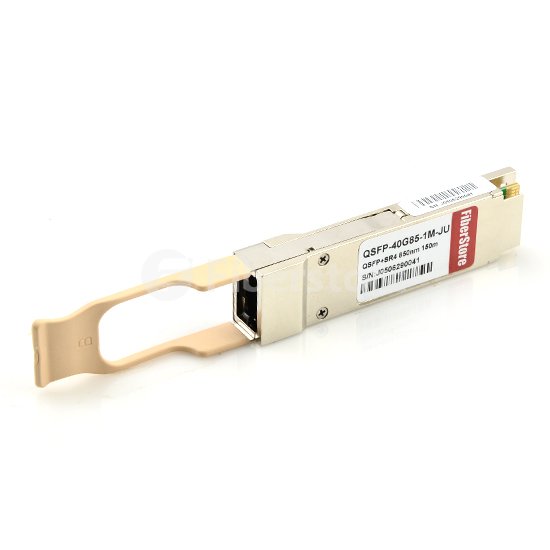
40 Gigabit Ethernet transceivers are being developed along several standard form factors. The C Form-Factor Pluggable (CFP) transceiver features 12 transmit and 12 receive 10-Gbps lanes to support one 100 Gigabit Ethernet port, or up to three 40 Gigabit Ethernet ports. Its larger size is suitable for the needs of single-mode optics and can easily serve multi-mode optics or copper as well. The CXP transceiver form factor also provides 12 lanes in each direction, but is much smaller than the CFP and serves the needs of multimode optics and copper. The Quad Small-Form-Factor Pluggable plus (QSFP+) provides four transmit and four receive lanes to support 40 Gigabit Ethernet applications. Fiberstore offers you a large amount of QSFP+ module options for you, such as Avago QSFP+, Brocade QSFP+, Dell QSFP+, Juniper QSFP+, Mellanox QSFP+, Finisar QSFP+, Intel QSFP+, ets. The picture below shows a Cisco QSFP-40G-CSR4 compatible 40GBASE-CSR4 QSFP+ transceiver.

One of the most attractive characteristics of 40 Gigabit Ethernet is broad applications and design flexibility. Considering the productivity gains and decrease in OpEx, migrating to 40 Gigabit Ethernet will prove very cost-effective for those who do it right. Fiberstore offers all kinds of cabling and transceiver choices for your 40G applications. You can buy from us with confidence.
Posted by: jowang at
06:54 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 667 words, total size 6 kb.
January 15, 2016
QSFP+ (quad small form-factor pluggable plus) cables offer a high density, high bandwidth, and cost-effective solution for a number of markets and applications. There are many kinds of QSFP+ cables. QSFP+ breakout cable is one of them. What is QSFP+ breakout cable? In this post, some basic information about QSFP+ breakout cables will be given.
To know whatQSFP+ breakout cableis, first you may ask what a breakout cable is. Breakout cable, or fanout cable, is an optical fiber cable containing several jacketed simplex optical fibers packaged together inside an outer jacket. Breakout cable is a hybrid solution. In a breakout cable, each fiber is individually reinforced, and each fiber is treated like a separate unit, so the cable can be easily divided into individual fiber lines. This design eliminates the necessity for a breakout kit, as the sheath allow you to attach connectors easily. It is different from distribution-style cable, in which tight-buffered fibers are bundled together, with only the outer cable jacket of the cable protecting them. The design of breakout-style cable adds strength for ruggedized drops than distribution-style cable. Breakout cable is suitable for short riser and plenum applications and for use in conduits.
A QSFP+ breakout cable consists of a QSFP+ transceiver on one end and four SFP+ transceivers on the other end. The cables are hot-removable and hot-insertable. QSFP+ transceiver connects directly into the QSFP+ access port on the QFX Series device. The cables use high-performance integrated duplex serial data links for bidirectional communication on four links simultaneously. And each SFP+ link is designed for data rates up to 10 Gbps. QSFP+ breakout cables create a great cost-effective interconnect way for IT professionals by giving much needed space for data centers and cost cuts.
There are many tyoes of QSFP+ breakout cable, here two commonly used kinds of them will be introduced, QSFP+ to 4SFP+ passive breakout copper cable and QSFP+ to 4SFP+ breakout active optical cable.
QSFP+ to 4 SFP+ passive breakout copper cable assemblies allow users to connect equipment with QSFP+ ports configured to work as four SFP+ ports. They offer a cost-effective, low-power option to support flexibility in high-speed data center applications. These high performance direct-attach assemblies support 4 lanes of 10 Gb/s (40Gb/s composite). These cables are the optimum solution for connecting your 40G QSFP+ and 10G SFP+ enabled host adapters, switches and servers without upgrading your entire data center or storage array.
QSFP+ to 4SFP+ breakout active optical cable is a 4×10Gb/s parallel active optical cable which transmits four separate streams of 10Gb/s data over ribbon cables in a point-to-multipoint configuration. It is commonly used for storage, data, and high-performance computing interconnectivity. The following shows a CiscoQSFP-4SFP10G-CU3Mcompatible QSFP+ to 4SFP+ passive breakout copper cable and a Cisco QSFP-4X10G-AOC10M compatible QSFP+ to 4SFP+ active optical breakout cable.
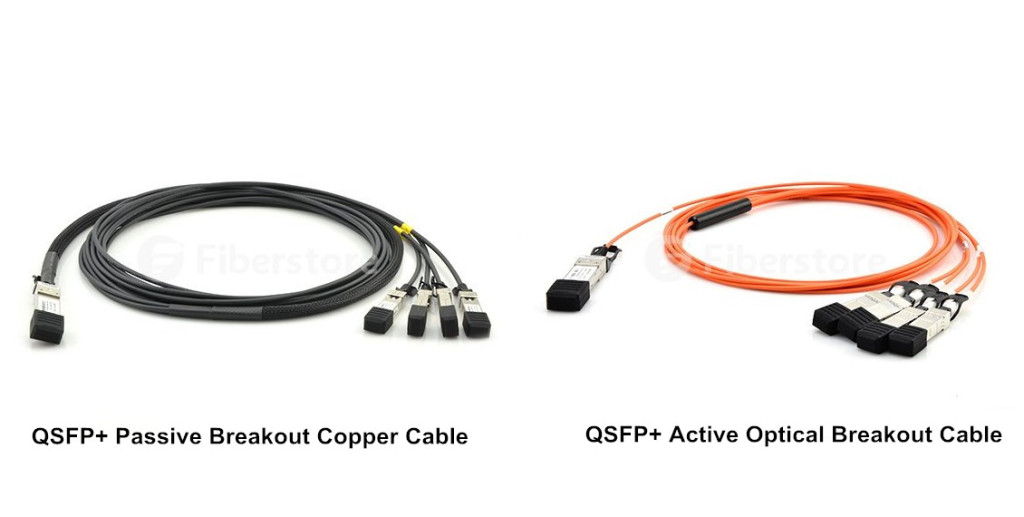

QSFP+ breakout cables permit you to connect your QSFP+ and SFP+ switches and network cards without upgrading your entire data center or storage array. The cables provide inexpensive and low power consumption interconnect solution for 40 Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel, QDR InfiniBand, 10 Gigabit applications and other industry standards.
Fiberstore provides QSFP+ to 4SFP+ passive copper breakout DAC, and QSFP+ to 4SFP+ breakout AOC. Custom cables can be found in various lengths along with other options. We currently provide several lengths to support your installation requirements. All our 40GBASE QSFP+ cables are 100% compatible with major brands like Cisco, Juniper and so on.
Posted by: jowang at
03:01 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 587 words, total size 6 kb.
January 12, 2016
QSFP+, quad small form-factor pluggable plus, is a compact, hot-pluggable transceiver used for data communications applications. 40G QSFP+ transceiver is a parallel fiber optical module, using four independent optical transmit and receive channels, offering users high-density 40 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity options for high-performance networks. Fiberstore offers a large amount of 40G compatible QSFP+ transceivers branded by many famous companies, like Cisco, HP, Juniper, and Brocade. In this post, some detailed information about HP 40G compatible QSFP+ transceivers will be given.
HP QSFP+is a Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) standard for high speed application, such as 40GBASE, which provides four channels of data in one pluggable interface. Each channel is capable of transferring data at 10Gbps and supports a total of 40Gbps. HP 40G QSFP+ transceivers enjoy several key features: QSFP+ MSA and SFF-8436 compatible, four independently addressable transmit and receive channels, highly compact and electrically hot-pluggable, digital diagnostic monitoring (DDM) interface for better module management, and simplified heat management with reduction in power consumption.
There are many kinds of HP QSFP+ transceivers to support different applications and transmit over various distances. Here are two commonly used types.
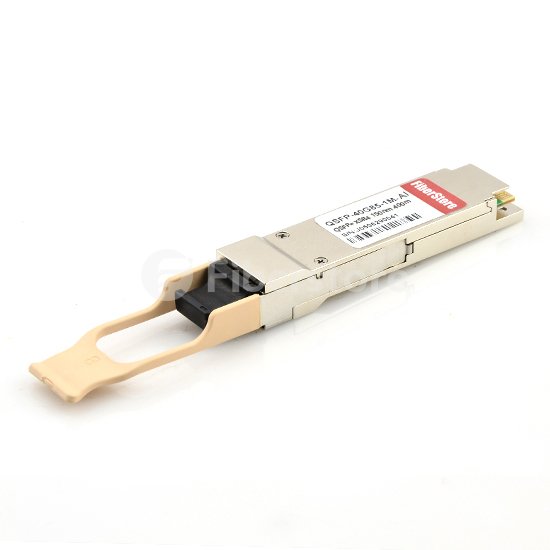
HP 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ Transceiver: HP 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ ransceiver supports link lengths of 100m and 150m, respectively on OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers at a wavelength of 850nm. It primarily enables high-bandwidth 40G optical links over 12-fiber parallel fiber terminated with MPO/MTP multifiber connectors and can also be used in a 4x10G module for interoperability with 10GBASE-SR interfaces. Digital optical monitoring (DOM) support is present to allow access to real-time operating parameters, which means, it is capable of performing transceiver monitoring and troubleshooting operations with DOM. The image below shows a HPJG325Bcompatible 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ transceiver.

HP 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ Transceiver: HP 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver enables high speed 4x10G operations. It is designed for use in 40 Gigabit Ethernet links over single mode fiber (SMF) with duplex LC connectors. It is compliant with the QSFP+ MSA and IEEE 802.3ba, and RoHS-6 compliant with built-in DDM interface. It primarily enables high-bandwidth 40G optical links with duplex LC connectors and can also be used in a 4x10G module for interoperability with 10GBASE-LR interfaces. Fiberstore compatible HP JG661A is intended to support up to 10km on single mode fiber cable at a wavelength of 1310nm. The image below shows a HP JG661A compatible 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver.
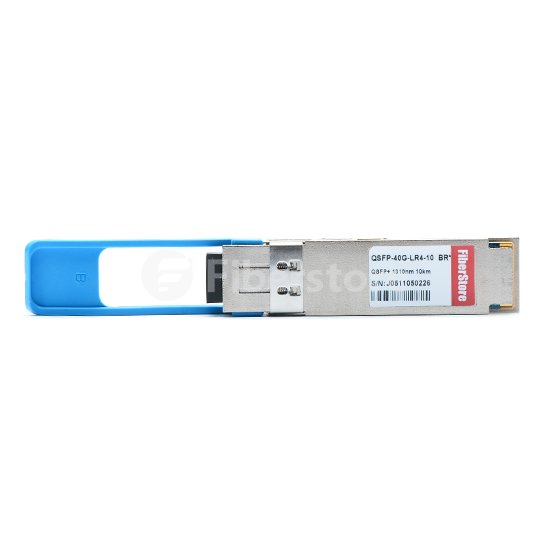

HP 40G QSFP+ transceivers are well suited for Infiniband, 40GBASE-SR4, 40GBASE-LR4 applications, suitable for short reaches among switches, routers and data center devices. Combined with right fanout cables, these modules can interface up to four SFP+ transceivers.
HP 40G QSFP+ transceivers features high-density and provide users with 40Gbps connectivity for better network performances. Fiberstore supplies various HP 40G QSFP+ transceivers with assured quality and performance. It is guaranteed to be 100% compatible with the equivalent HP optics module. FS.COM stands behind the quality of our products and proudly offer a limited lifetime warranty.
Posted by: jowang at
06:40 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 502 words, total size 6 kb.
January 08, 2016

Internet exchange services provider DE-CIX reports that its flagship Frankfurt Internet exchange hit an active traffic peak of 5 Tbps on December 8, 2015. The traffic flow was a new record for the exchange, which topped 4 Tbps the previous April (see "DE-CIX touts 4-Tbps traffic peak at Frankfurt Internet exchange").
Besides having the requisite number of customers, DE-CIX attributes the 5-Tbps benchmark to the rapid worldwide growth in data demand, driven predominantly by video and Internet-enabled mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
"We are surprised ourselves how strongly our customer capacities have ramped up this year and how much the data traffic on our Internet exchange in Frankfurt has grown," stated Harald A. Summa, DE-CIX CEO, via a press release issued shortly after the highpoint was reached. "In total, the capacity booked by our customers at DE-CIX Frankfurt has increased by 40.3%, from 12.9 terabit at the beginning of the year to 18.1 terabit today. So far [in 2015], we've also booked more than fifty 100GbE connections that is double the number we'd expected for the entire year. Additionally, through the end of the year, we will have connected more than approximately 100 new networks."
DE-CIX points out that the Frankfurt Internet exchange has a capacity of 48 Tbps, so it should be able to accommodate the current growth curve for some time to come.
In addition to the Frankfurt facility, DE-CIX operates a number of exchanges around the world. Locations include Hamburg, Munich, New York, and Dubai, which in 2015 were joined by Dallas, Dusseldorf, Istanbul, Marseille, and Palermo (see, for example, "DE-CIX targets Instanbul for Internet exchange" and "TI Sparkle, DE-CIX establish neutral Internet exchange in Palermo").
Posted by: jowang at
03:50 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 295 words, total size 3 kb.
January 06, 2016
There are many kinds of optical transceiver in the market. When looking at a transceiver module, you may see words like 1000BASE-CX, 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-T, and so on. For example, the following picture shows a 3CSFP91 compatible SFP transceiver. You can see "1000BASE-SX SFP" on it. What do they mean? And what's the difference between 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-CX, and 1000BASE-T? In this post, a brief introduction to 1000BASE will be given.
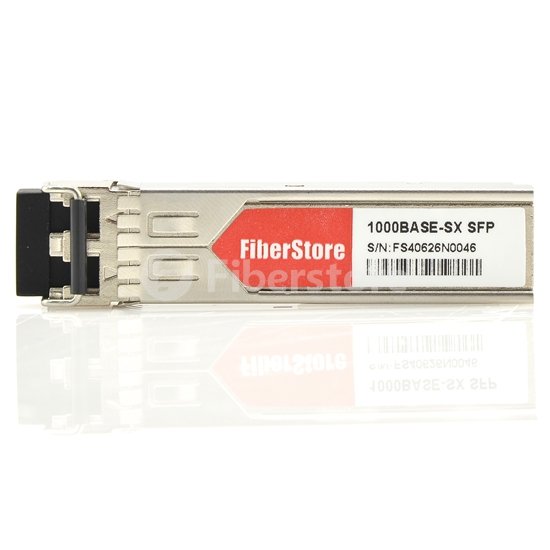

The "1000" refers to the transmission speed of 1000Mbps. In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GE or 1GbE) is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second, as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. The cables and equipment are very similar to previous standards and have been very common and economical since 2010. You may wonder what the word "BASE" means. BASE refers to "baseband", meaning that this is an unfiltered line not requiring a digital modulation scheme. Back in the day, there was a 10PASS-TS version of Ethernet that used a signaling scheme similar to a modem, but baseband is dominant today. So 1000BASE refers to a Gigabit Ethernet connection that uses the unfiltered cable for transmission.
The next part is the cabling used to carry the signals. The earliest forms of Ethernet used coaxial cable, but thin twisted-pair cabling became popular in the mid-1990s. Faster versions of Ethernet also often use fiber optics rather than electrical signals. There are a bewildering assortment of physical interconnects for Ethernet. But the naming system isn't as complex as it might appear. The first letter tells us which kind of wire we are talking about:
- "S" means short-range multi-mode optical cable (less than 100 m)
- "L" means long-range single- or multi-mode optical cable (100 m to 10 km)
- "E" means extended-range optical cable (10 km to 40 km)
- "Z" means long-range single-mode cable at a higher wavelength
- "T" means twisted-pair cable (e.g. the common Category 5 in use today)
- "K" means a copper backplane
- "C" means balanced copper cable
- "B" uses two wavelengths over a single optical cable
Next is the coding scheme for data on the wire: "X" means 8B/10B block coding for Gigabit Ethernet. Then, we have a number representing the number of parallel "lanes" for data: "1" would mean serial (non-parallel) but is omitted instead; "4" or "10" are available for copper wire; just about any other number could be used for optical lanes or wavelengths. As you can see, common unshielded twisted pair wiring is "BASE-T", optics are denoted according to their range ("S", "L", "E"), and backplanes use "K" copper.
1000BASE-SX standard is a variant coupled to a VCSEL laser with a short wavelength of 850nm. It has a maximum length of 550 meters. 1000BASE-SX technologies are being widely implemented in enterprise-level networks and primarily used between pieces of equipment within a building. 1000BASE-LX standard has a working distance of up to 5 km over single-mode optic fiber. And it can also be used to transmit data over common multi-mode fiber options with a maximum length of 550m. 1000BASE-EX standard is capable of transmitting up to 40 km over a single-mode optic fiber pair due to higher quality optics. 1000BASE-CX is an initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet connections with maximum distances of 25 meters using balanced shielded twisted pair. 1000BASE-KX standard is for Ethernet operation over electrical backplanes. It defines one to four lanes of backplane links, one RX and one TX differential pair per lane. The 1000BASE-KX variant uses 1.25GBd electrical (not optical) signalling speed. 1000BASE-T normally uses four pairs of the commonly installed Category 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable or enhanced category 5 cabling version of UTP cabling to achieve gigabit data rates. The image below shows a Moxa SFP-1GLSXLC 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver.
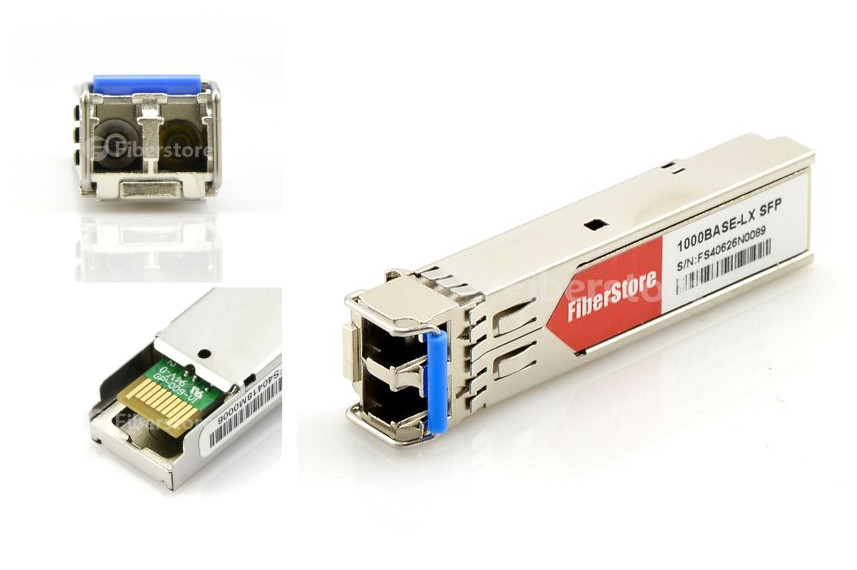

There are various 1000BASE SFP transceivers available depending on the your application and distance capability required. Fiberstore is a professional manufacturer and supplier, offering various kinds of 1000BASE SFP transceivers 100% compatible with major brands like Cisco, HP, Juniper, Force10, D-link, 3Com. They are backed by a lifetime warranty, and we also can customize optical transceivers to fit your specific requirements.
Posted by: jowang at
06:38 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 694 words, total size 7 kb.
January 04, 2016
Fiber optic transceivers are used to send and receive optical information in a variety of different applications. These devices help designers in a variety of different applications including telecommunications. The devices are scalable and flexible in their use. They are preferred by designers. There are many kinds of fiber optic transceivers in the market. Which one to choose? Here are some tips on how to select the best type of fiber transceivers.
There are two modes of fiber to consider: single-mode and multi-mode. Single-mode fiber optic cable is used in applications that need bandwidth that will travel over long distances. Multi-mode fiber will allow each signal to travel on more than one pathway at one time. There are numerous different types of multi-mode fiber that have all types of bandwidth capacity.
There are four basic types of internal construction, in which you need to choose the one that will work best for your application. One of the most popular types is the distribution or tight pack. The second type is the breakout or fan-out design, which gives each buffered fiber its own individual jacket and is a more durable design. The zip cord or assembly is another preferred internal construction option. In this construction, one or two buffered fibers in individual jackets should be considered. The loose tube is the final option. In this design, non-buffered fibers are threaded through a tube along with a water repellent gel compound. The image below shows an AT-SPLX10 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver.
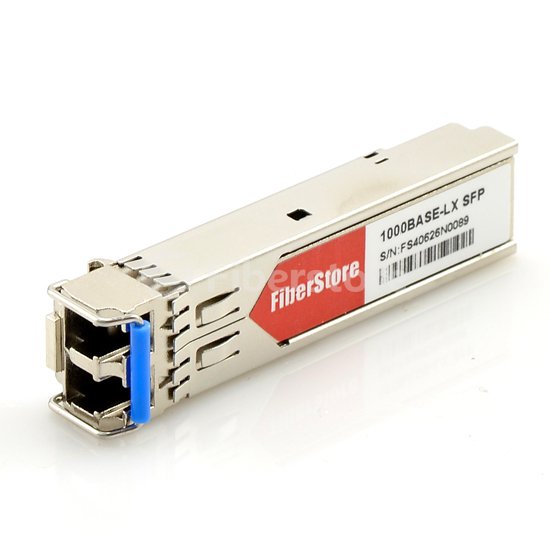

Some transceiver types will cause major loss and conflict. Many chips only use the full-duplex configuration and are not capable of supporting the half-duplex environment. Using the wrong type of fiber transceiver for an application, like using a half-duplex when the application requires full-duplex, will cause significant loss or conflict. Only choose full-duplex unless you think that your application can support half-duplex.
Fiber optic transceivers will produce high temperatures when they are not operating properly. Transceivers may fail prematurely at high temperatures. What are the thresholds for your devices? The higher the threshold, the more flexible the device will be in various applications. Temperature adaptability should be high for the best performance. It is important to know how well a transceiver can adapt to heat if it will be in high temperatures.
Some manufacturers of transceivers incorporate the use of a safety device to prevent packet loss. This is preferable to many different types of designers. Other designers skip this feature to reduce costs. This is not preferable and can result in an inferior design. In some instances, it’s better to increase costs than to remove devices to save money. Find transceivers with safety measures to decrease the probability of packet loss.
It is not always easy to know which type of transceivers should be chosen for which applications. There are a variety of factors that must be considered, including the internal construction, fiber mode, fiber cable jackets, and the temperature adaptability. Fiberstore provides a full range of optical transceivers, such as SFP+, X2, XENPAK, XFP, SFP, GBIC transceiver, CWDM/DWDM transceiver, 40G QSFP+, WDM Bi-Directional transceiver and PON transceiver. All our fiber transceivers are 100% compatible with major brands like Cisco, Finisar, HP, Juniper, Force10, D-link, 3Com. For example, Cisco MFEFX1 100BASE-FX SFP transceiver, Finisar FTLX8512D3BCL 10GBASE-SR/SW XFP transceiver, and NETGEAR AXM761 10GBASE-SR SFP+ transceiver, they are all backed by a lifetime warranty, and you can buy with confidence.
Posted by: jowang at
06:30 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 590 words, total size 6 kb.
32 queries taking 0.071 seconds, 88 records returned.
Powered by Minx 1.1.6c-pink.









