August 12, 2016
New technology advances in networking, such as 10G, 40G and 100G Ethernet solutions, mean that data center administrators face new challenges: maintaining high availability, reducing costs, seeking out higher efficiency and planning for future growth. Fiber optic patch cable, the key component in fiber optic communication system is designed to interconnect or cross connect fiber networks within structured cabling systems. It is used in data centers to interconnect ports and transceivers that accept LC and MPO/MTP fiber optic connectors. FS.COM offers a full range of cost-effective fiber patch cable solutions which can meet today and future growth. This article will demonstrate FS.COM high-speed fiber patch cable solutions for 10G, 40G, and 100G Ethernet transceiver ports interconnection as well as the cost-effective fiber patch cable solution for high-density patching.
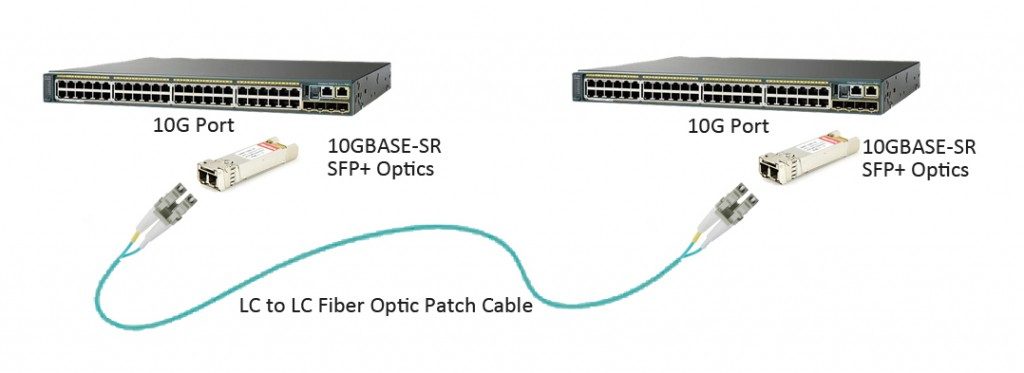
Today’s data centers are still primarily architected around 10G Ethernet. After almost ten years of revolution, SFP+ gradually becomes the main stream of 10G transceiver in data center optics market. According to the optical ports of SFP+ form factor, the duplex LC patch cable is required to complete the link between two SFP+ modules which are plugged into switches, routers or server NICs (Network Interface Cards). FS.COM offers high quality standard LC duplex patch cables which are available in single-mode and multimode patch cable. With a wide range of material options, they can meet any working environment.
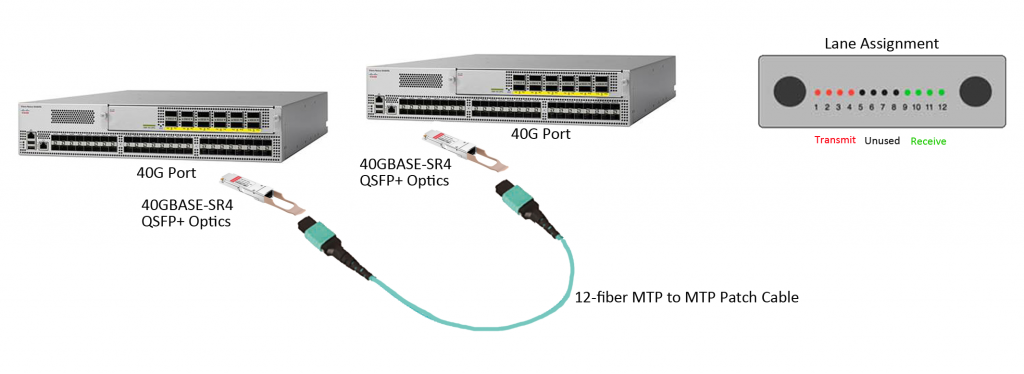
40G transceivers are ramping up hard as data centers deploy 40G Ethernet. QSFP+ transceivers, as the most popular form factor, are being widely used in data center switching fabrics. For the short reach interconnection between two QSFP+ ports, each QSFP+ transceiver requires an MPO/MTP connection. FS.COM offers MTP to MTP (or MPO to MPO) assemblies in multimode or single-mode version, with jacket ratings of riser, plenum and LSZH. With popular multimode OM3 and OM4 cable assemblies, users can easily upgrade to future 40/100G applications.
For single-mode 40G QSFP+ interconnection, it is commonly used with duplex LC single-mode patch cable. But for 40GBASE-PLRL4 QSFP+, a 12-fiber MPO/MTP single-mode cable is needed. As we know, a single QSFP+ port (4 x 10 Gbps) can breakout to four SFP+ port. Thus, using FS.COM MPO/MTP to LC assembliescan easily achieve the migration of 10G to 40G.
100G is considered the trend of the year of 2016. 100G transceivers including CXP, CFP, CFP2, CFP4 and QSFP28 are available for different applications. For applications requiring data rates of 100G, FS.COM provides multiple cost-effective solutions as follows:
- CXP/CFP to CXP/CFP InterconnectionFS.COM’s 24-fiber MPO/MTP assemblies are ideal for 100GBASE-SR10 CXP/CFP to CXP/CFP interconnection in data center, since it is implemented 10 lanes of 10 Gbps. Among the 24 fibers, only 20 fibers in the middle of the connector are used to transmit and receive at 10 Gbps and the 2 top and bottom fibers on the left and right are unused.
- QSFP28 to QSFP28 InterconnectionThe QSFP28 is the exact same footprint as the 40G QSFP+, but is implemented with four 25Gbps lanes. To interconnect a multimode QSFP28 link, a 12-fiber MPO/MTP patch cable is required, while for single-mode link (100GBASE-LR4 QSFP2
 , a duplex LC single-mode patch cable is required. The interconnection of QSFP28 multimode link is similar with the case of 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+.
, a duplex LC single-mode patch cable is required. The interconnection of QSFP28 multimode link is similar with the case of 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+. - CXP/CFP to 10 x SFP+ InterconnectionAs mentioned above, 100GBASE-SR10 CXP/CFP uses ten 10Gbps lanes to achieve 100Gbps data rate. Thus, a CXP/CFP port can be breakout to ten SFP+ ports using 24-fiber to LC harness cables from FS.COM.
High-density patch cables are with higher performance and easier to use compared to common ones. FS.COM offers a wide range of high-density fiber patch cables, such as LC-HD and MPO-HD TAB fiber patch cable, Keyed LC fiber patch cables, LC uniboot fiber patch cables, bend insensitive fiber patch cables, etc. All these patch cables are with high performance and can be customized according to specific requirements.
Posted by: jowang at
10:36 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 656 words, total size 6 kb.
August 08, 2016
In the past few decades, Ethernet standard continuously evolves to meet the increasing demand for faster transmission speed, from 100BASE, 1000BASE to 10GBASE. At the same time, the data carrying technology also develops to provide great bandwidth for transporting data with low cost, such as the copper and fiber cables as well as optical transceiver modules.
In 10 Gigabit Ethernet, copper and fiber are used to transport data. Each one has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Copper is more cost-effective and easier to install. It suits best in short lengths applications, typically 100 meters or less. But when deployed over long distance, electromagnetic signal characteristics will influence its performance. Besides, bundling copper cabling can cause interference, making it difficult to employ as a comprehensive backbone. So copper cabling is widely used in PCs and LANs communication network instead of campus or long-distance transmission.
Compared with copper, fiber cabling is usually used for long distance communication among campus, and environments that need protection from interference, such as manufacturing areas. In addition, fiber cabling is more reliable and less susceptible to attenuation, which makes it suitable for data transmission distance over 100 meters. But fiber still has drawbacks. It’s more costly than copper.
Since 10 GbE technologies have changed, so have the cabling technologies. There are two main standards: IEEE802.3ae and IEEE802.3ak. Factors covered in these standards like transmission distance and equipment being used are helpful to determine the cabling strategy.
- IEEE802.3aeIEEE802.3ae standard updates the existing IEEE802.3 standard for 10GbE fiber transmission. The new standard defines several new media types for LAN, metropolitan area network (MAN) and wide area network (WAN) connectivity.
10GBASE-SR – it supports 10GbE transmission over standard multimode fiber (850 nm) for distances of 33 and 86 meters. The SR standard also supports up to 300 meters using the new 2000MHz/km multimode fiber (laser optimized). For example, the HPE J9150A 10GBASE-SR SFP+ transceiver from FS.COM can achieve the max distance of 300m over OM3 multi-mode fibers.
10GBASE-LR – it uses optics (1310nm) and supports single-mode fiber up to 10 km.
10GBASE-LX4 – it can support multimode fiber for distances up to 300 meters using Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM). The LX4 standard also supports single-mode fiber for up to 10 Km. LX4 is more expensive than both SR and LR because it requires four times the optical and electrical circuitry in addition to optical multiplexers.10GBASE-ER – it uses optics (1550nm) to support single-mode fiber up to 30 km.
- IEEE802.3ak / 10GBASE-T10GBASE-T is the latest proposed 10GbE standard for use with unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) style cabling. This standard is to improve the performance and increase the transmission distance at a lower cost. Category 5 (Cat 5) and Category 6 (Cat 6) are the most common cabling systems being installed today. But Cat 5 can’t meet the bandwidth demands of 10GbE’s transmission. To meet the needs of 10GbE, manufacturers create Category 6A (Cat 6A), designed with existing Cat 6 cable but measured and specified to higher frequencies. In addition to Cat 6A, 10GBASE-T will operate on Category 7 (Cat 7) cables.
Except the cabling, transceivers also need to be considered for the network connectivity. Transceivers provide the interface between the equipment sending and receiving data. 10GbE has four defined transceiver types, including XENPAK, X2, XFP and SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus). These transceivers are pluggable and are compliant with 802.3ae standard.
Among them, SFP+ is the smallest 10G form factor. And it can interoperate with XENPAK, X2, XFP interface on the same link. Fiberstore provides a number of interfaces attempted to satisfy different objectives including support for MMF and SMF compatibility, such as SFP-10G-SR, SFP-10G-LR, SFP-10G-ER, SFP-10G-ZR, etc. For example, SFP-10G-SR transceiver module can support 300 meters data transmission distance over 850 nm multimode fiber. And SFP-10G-LR module (eg. J9151A) supports the link length up to 10 kilometers over 1310 nm single mode fiber.
As the 10G cabling technologies improved and 10G costs decreased, the 10G connectivity market has already mature. FS.COM provides detailed 10G connection solutions, including optical transceivers, patch cables, cable management products for transmission over both long and short distances. Each optics here is fully tested to ensure its 100% compatibility.
Posted by: jowang at
09:28 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 710 words, total size 6 kb.
32 queries taking 0.049 seconds, 68 records returned.
Powered by Minx 1.1.6c-pink.









