June 03, 2016
Deploying fiber optic jumper cables is just the first step to meet the high-bandwidth requirements, and efficient and strong management over those fiber optic patch cords is the basic requirement for a successful fiber optic network infrastructure. To deliver and guarantee the optimal network performance, fiber patch cable management is critical. Good management can lower operation cost and time, and increase the reliability and flexibility of network operation and maintenance. This post will help you better understand fiber patch cable management.
To get a flexible and well-organized fiber patch cable management, you need to take several factors into consideration.
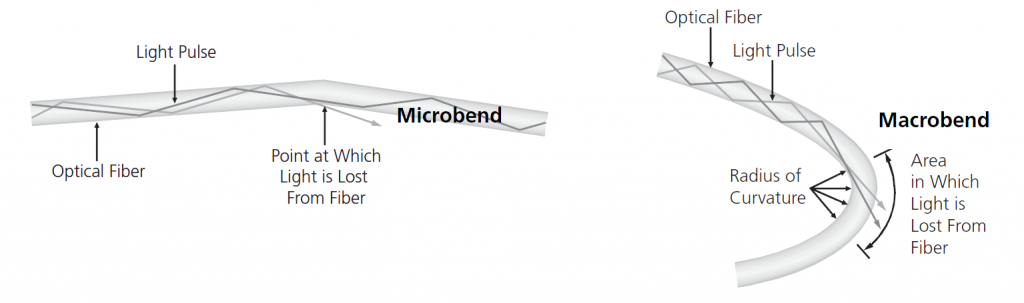
Bend RadiusCompared with copper, optical fiber, usually made of glass, is much more fragile and need more protection and attention during the operation and management. Bend radius of an optical fiber will impact its reliability and performance. If a fiber cable is bent excessively, optical signals within the cable may refract and escape through the fiber cladding, causing loss of signal strength, also known as bend loss. Bending, especially during the installation and pulling of fiber optic patch cable, may also cause micro cracks and damage the fiber permanently. There are generally two basic types of bends, which are microbends and macrobends, as shown in the following picture.
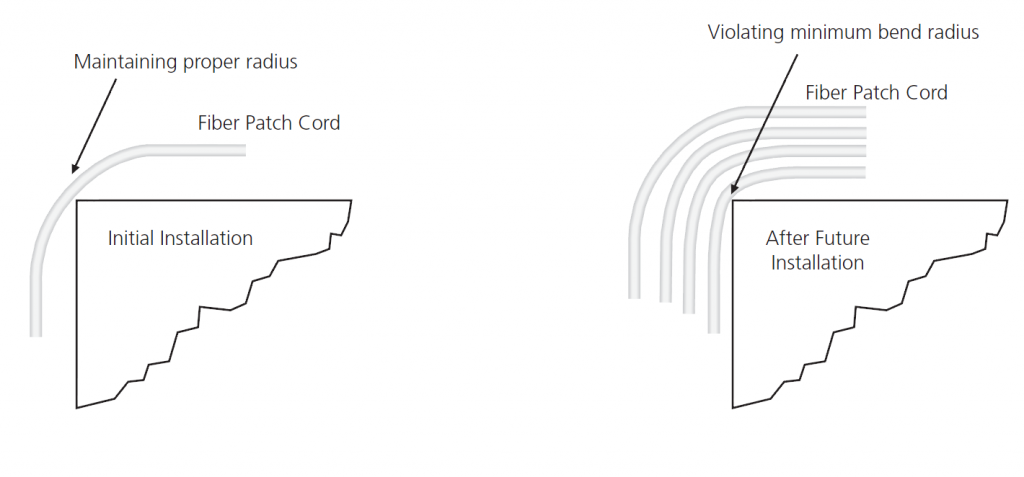
Note that bend radius might not be seen during the initial installation of fiber patch cables. Because the number of fiber patch cables routed to the optical distribution ODF is usually small. When more fiber patch cords are added on the top of installed fiber patch cables later, problems will show up (shown in the following picture). A fiber patch cable which works fine for years might suddenly have an increased level of attenuation, as well as a potentially shorter service life.
Fiber patch cable path, which can affect the performance and maintenance of fiber patch cables, is an aspect closely related to bend radius. The path of fiber patch cable should be clearly defined and easy to follow. Improper cable routing can cause increased congestion in the termination panel, increasing the possibility of bend radius violations and long-term failure. Well managed fiber patch cable path ensures that bend radius requirements are maintained at all points and makes access to individual fiber patch cable much easier, quicker and safer, especially for those fiber patch cables with different types of connectors on the two ends, such as SC to LC fiber cable, or LC to ST fiber patch cable. Well-organized fiber patch cords can also help to decrease operating costs and the time required to turn-up or restore service.
Accessibility of Fiber Patch CableAccessibility of the installed fiber patch cable is also a factor that you need to take into consideration. If installed fiber patch cables are easy to access, the maintenance and operation would be quick without inducing a macrobend on an adjacent fiber, and it can also offer proper bend radius protection. Accessibility is critical during network reconfiguration operations and directly impacts operation costs and network reliability.
According to those mentioned aspects which can affect the performance and maintenance of fiber optic patch cables, here are several tips that can help to increase the performance of fiber patch cords and the reliability and flexibility of fiber patch cable management.
- 1. Pay attention to the bend radius of fiber patch cables. Generally, for 1.6mm and 3.0mm fiber patch cords the minimum un-loaded bend radius is 3.5cm. The minimum bend radius of MPO cable is ten times the cord diameter.
- 2. Never pull or stress fiber patch cords. During the patching process, excessive force can stress fiber patch cables and connectors attached to them, thus reducing their performance. There might be something wrong if you need to use force in pulling a cord.
- 3. Routing fiber patch cords through cable pathways, so as to ensure there are no tangles, kinks or strains in the cords. For efficient routing, find the best path between the ports to be connected, avoiding routing cords through troughs and guides that are already congested.
- 4. Bundling and tying fiber patch cords gives the panel a neat appearance but tight bundling increases the risk of pinching. Do not tighten cable ties beyond the point where individual cord can rotate freely.
- 5.Labeling is necessary. At any administration point in a cabling infrastructure, including patching panels, accurate labels are essential. These will identify pair modularity and tell technicians where the other end of the cable is terminated.
- 6. Inspect fiber patch cords for physical damage including stress marks from sharp bends on the sheath, or damage to connectors.
A successful fiber patch cable management can increase the reliability and flexibility and decrease the cost of network operation and maintenance. To achieve successful fiber patch cable management, you need to consider and ensure bend radius protection, reasonable patch cable paths, and easy accessibility to fiber patch cables. When those factors are satisfied, it is already half the success to strong fiber patch cable management.
Posted by: jowang at
02:59 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 843 words, total size 7 kb.
35 queries taking 0.0197 seconds, 70 records returned.
Powered by Minx 1.1.6c-pink.









